Bios Fundamentals: Everything You Need to Know About a Laptop's Bios
Introduction
Understanding your laptop's BIOS (Basic Input Output System) can be a game changer when it comes to troubleshooting and performance optimization. This guide is designed to break down the concept of BIOS, its roles, how it works, and how it compares to firmware. Additionally, we will point out how to access and update your BIOS. Stay tuned to get answers to frequently asked questions about BIOS.
What is BIOS on a Laptop?
BIOS, that stands for Basic Input Output System, is a quintessential piece of firmware pre-installed in your laptop's motherboard. Its role is initiated as soon as you power up your device, and it persists right until your operating system is ready to take over. Here's a breakdown of BIOS actions:
- Initialization: BIOS springs into action, initializing the hardware components in your system. This process is commonly known as 'POST' or Power-On Self Test.
- Hardware Testing: During POST, BIOS verifies that all hardware components are functioning as they should.
- Locating the Operating System: Once the POST is successfully completed, BIOS goes a step further to locate the operating system on your storage device.
- Loading of OS Instructions: BIOS then undertakes the task of loading into memory a segment of the hard disk responsible for carrying out the operating system's instructions.
BIOS is the unsung hero firing up your laptop every time you switch it on, setting the stage for your operating system to perform. Once BIOS has done its job, the operating system's booting process is initiated, culminating in the creation of a user interface to interact with your laptop.
Understanding the Role and Functions of BIOS
The BIOS is a powerful piece of software that plays several critical roles in your laptop's operation. These central functions help maintain your device's smooth running and enable user control over key system settings:
• Power-On Self Test (POST): As the machine is powered on, the BIOS first performs the POST. This hardware verification procedure confirms the operational status of key system components.
• Identifying the Operating System: The BIOS's next role is to locate the laptop's operating system. Stored on your device's hard drive, BIOS identifies the Master Boot Record (MBR) that contains the operating system.
• Loading of the Operating System: Upon identification, the BIOS proceeds to load the operating system into the laptop's memory. This prepares the system's user interface for subsequent operations.
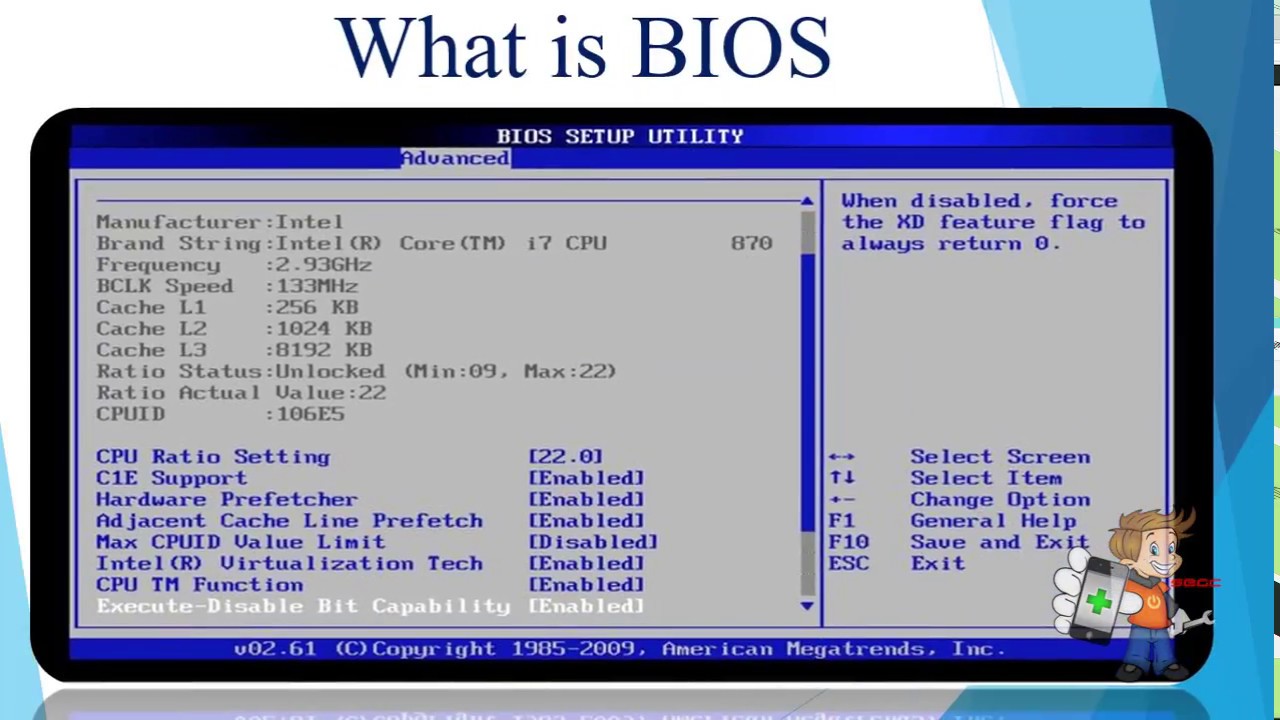
• System Settings Control: Lastly, the BIOS houses vital system settings including time, date, and hardware configurations. Accessing the BIOS allows users to customize these settings to their preference, providing a tailored computing experience.
Understanding these functions provides valuable insight into the indispensable operation of BIOS on your laptop. From power-on to shut down, the BIOS functions continuously behind the scenes, ensuring your device works optimally.
How Does BIOS on Your Laptop Work?
The BIOS is integral to your laptop's operation. Let's dig a little deeper and understand the steps involved in BIOS operations:
1. Power On: You press the power button on your laptop. This action triggers the BIOS into action, marking the start of the booting process.
2. POST – Power-On Self-Test: This is the initial phase where BIOS verifies the integrity of hardware components. It checks your laptop's hard drive, memory, processor, and peripheral devices. If all systems are go, the boot process proceeds to the next stage.
Key Indicator: If there's an issue with any hardware component, the BIOS will alert you via an error message or audio code.
3. Locate Boot Loader: BIOS scans your hard drive for the Master Boot Record (MBR). Within the MBR lies the boot loader, a small program responsible for loading your operating system.
4. OS Activation: After successfully locating the boot loader, BIOS loads the operating system into your system's memory, bringing your laptop to life. The control is then handed over from the BIOS to the operating system.
5. System Settings Maintenance with CMOS: BIOS uses CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) to save all system settings. This memory is kept alive by a small battery on your laptop’s motherboard, sustaining your system settings even when powered off.
Note this: If your laptop forgets time and date settings or behaves unusually after powering off, it's often a sign of a depleted CMOS battery.
Compact and succinct, that’s how BIOS works on your laptop!
BIOS Vs Firmware: Key Differences & Similarities
BIOS and firmware, although similar, still display distinct characteristics. To help clarify, we've broken down their key differences and similarities, as listed below:
Differences:
- Scope: BIOS is a type of firmware that's used explicitly within computers. Firmware, however, extends its utility to a wider range of devices such as cameras, televisions, and even household appliances.
- Functions: BIOS plays a pivotal role in initiating the boot process and ensuring smooth hardware-software interaction in a computer. On the other hand, firmware controls how the embedded hardware in devices functions.
Similarities:
- Type: Both BIOS and firmware are types of software, but they are stored in the hardware.
- Role: They're fundamental to device operation as they control how the hardware in the respective devices works.
- Storage: Typically, both BIOS and firmware are written onto read-only memory to protect against unauthorized modification.
Understanding the distinction and relationship between the two can lead to a broader comprehension of your device's functioning and improve troubleshooting efficiency.
How to Access and Update BIOS on a Laptop?
Ensuring that your laptop's BIOS is up-to-date is integral to its smooth performance. This process might seem daunting, but it's in fact simple to carry out by following these carefully arranged steps:
How to Access BIOS?
1. Restart your laptop. As your system powers up, pay keen attention to the screen for prompts relating to the 'setup' or 'BIOS'.
2. Upon noticing these prompts, press the indicated key to enter BIOS. Usually, the key will be F10, F2, DEL, or a similar button, depending on the laptop model.
Be aware, this interaction is time-sensitive and must take place before the operating system starts to load.
How to Update BIOS?
Once you have access to the BIOS, follow these next steps.
1. Confirm Your BIOS Version: You need to know your current BIOS version to make sure you get the correct update. You can typically find this information within the BIOS interface or on the diagnostic page in Windows.
2. Get The Update: Head to your laptop manufacturer’s website. Navigate to its support section and locate your model. Download the most recent BIOS update available.
3. Proceed With The Update: Execute the downloaded BIOS update file. This may be an executable that will automate the update process or an update file that you will need to load through your BIOS.
4. Follow The Guides: Ensure you follow the manufacturer's instructions to the latter. Remember, any error in updating BIOS might render your laptop unbootable.
Keep in mind that while updating BIOS generally improves system performance and can fix existing bugs, it can occasionally introduce new conflicts. Consequently, only consider an update when it's necessary, such as to fix a specific issue or to support a newly installed component. Always remember that a successful BIOS update enhances your laptop's operational efficiency and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Knowledge of BIOS fundamentals paves the way for better understanding and troubleshooting your laptop's technical snags. The BIOS is your laptop's unsung hero, bridging the gap between the hardware and software, keeping your system up and running. Knowing how to manage it can lead to superior laptop performance and longevity. Although BIOS operations occur behind the scenes, they are part and parcel of your everyday computing experience.
Related FAQs about what is bios on a laptop
What is the difference between BIOS and UEFI?
BIOS and UEFI are firmware interfaces for computers. BIOS is an older system and works in a 16-bit processor mode, whereas UEFI operates in 32-bit or 64-bit mode, allowing for a faster startup and better hardware support. UEFI also includes secure boot capabilities, which can protect a system against boot-time malware or rootkit attacks.
How can I troubleshoot common BIOS issues?
Troubleshooting common BIOS issues may involve resetting BIOS settings to default, clearing the CMOS memory, updating BIOS, or troubleshooting hardware related issues. It's important to remember that changing BIOS settings should be done carefully, as wrong alterations can lead to system instability.
Is it necessary to update BIOS on a laptop?
While updating BIOS can improve system performance and resolve bugs, it can also sometimes introduce new issues. Therefore, unless you're experiencing a specific problem that an update would fix, or support for a new hardware component is needed, it's generally recommended not to update BIOS frequently.


