Unlocking the Secrets of Your Camera: Understanding What is a Camera Image Sensor
Introduction
Demystifying your camera starts with unlocking the secrets of its key components. Among them, understanding the image sensor plays a crucial role in capturing images that are true to your perspective. In this guide, we will delve into the world of camera image sensors, revealing the types available, how they impact image quality, and why their size matters. By the end, you will have all you need to know to choose the right sensor for your photography needs.
What is a Camera Image Sensor?
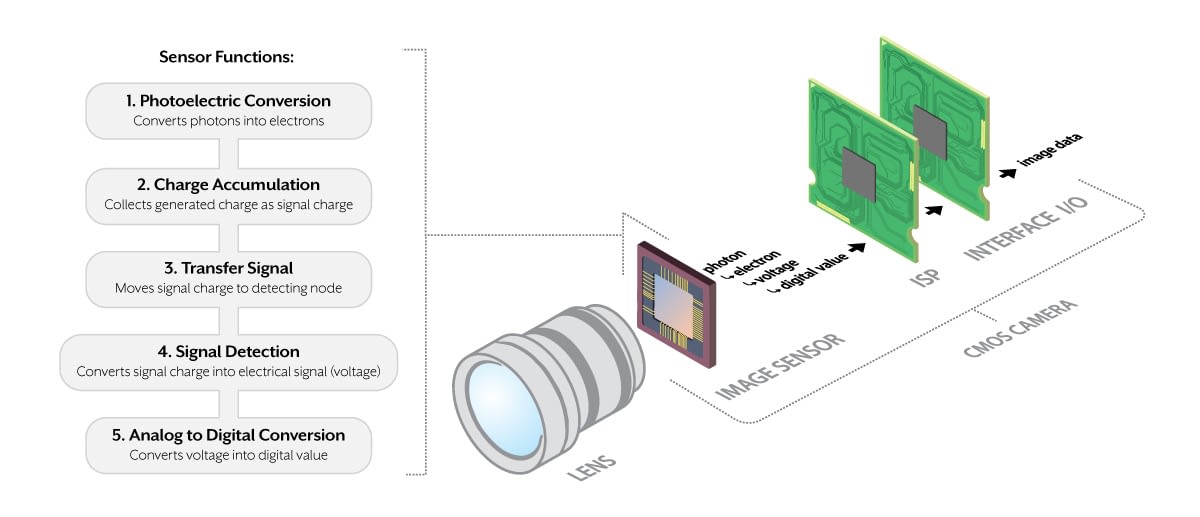
At the heart of digital photography lies a critical device known as the camera image sensor. This technological marvel serves as the core component of digital cameras, embodying the following important characteristics:
- It's a light-sensitive surface that's home to millions of pixels. These pixels do the heavy lifting when it comes to picture capturing; they take incoming light from the lens and create an image.
- Each pixel on the sensor converts received light into an electrical charge. This charge is then rendered into digital data, bringing to life the images we view on screens or printed photos.
- The image sensor is essentially the digital equivalent of film in traditional photographic equipment. Its main role is light capture - converting it into digital images.
By engaging with these fundamental aspects of a camera image sensor, you will start to see how this component sits at the center of the camera's image-capturing arsenal. It's vital, therefore, to comprehend its workings to optimize the quality of captured images and understand what lies behind creating stunning photos. In essence, the image sensor is the core mediator between reality and the digital representation that we view as a photo.
What Types of Camera Image Sensors Are There?
If you've ever delved into the world of digital cameras, you'd have most likely come across the terms: CCD and CMOS. These pertain to the primary types of camera image sensors that dominate the photography landscape.
- CCD (Charge-Coupled Device): This type of sensor is well-celebrated for its unmatched image quality. Cameras equipped with CCD sensors have the ability to generate high-quality, low-noise images. Though it promises excellent picture clarity, one downside to this kind of sensor is its relative expense.
- CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor): The CMOS sensor is generally the more cost-effective counterpart to the CCD sensor. What it lacks in image quality as compared with CCD, it makes up in affordability and power efficiency. The CMOS sensor's functionality presents significant improvements when it comes to capturing high-speed photography.
Moving beyond the CCD vs CMOS debate, there are also variations in the size of image sensors which significantly affect the output image:
- Full-Frame Image Sensors: Mimicking the size of a 35mm film, full-frame sensors offer superior images and are ideal for professional photographers.
- APS-C Sensors: A notch smaller than full-frame sensors, APS-C sensors are nonetheless lauded for their high-quality images. Offering an economical alternative to full-frame sensors, they remain a favorite amongst budding photographers.
How Does a Camera Image Sensor Impact Image Quality?
The camera image sensor plays a significant role in determining the quality of the images you capture. It's important to grasp how its size, resolution, and type directly contribute to overall image quality.
1. Size: The size of the image sensor is fundamental in capturing light during the exposure. Larger sensors can capture more light, extending the convenience of low-light photography and lowering image noise. For instance, a full-frame sensor, considerably larger than APS-C sensors, can offer better image quality because it gathers more light.
2. Resolution: High-resolution sensors can capture more detail, enabling your photographs to remain crisp and clear, even when enlarged. For example, a camera with a 20MP sensor can capture more details compared to a camera with a 12MP sensor.
3. Sensor Type: The type of sensor your camera uses can also influence image quality. CCD sensors are known for producing high-quality, low-noise images, ideal for static photography. On the other hand, CMOS sensors, while generally less expensive than CCD, render improved performance in high-speed photography.
Here's a look at how these factors impact image quality:
- Larger Sensors: Higher dynamic range, reduced image noise, better low-light performance, enhanced depth of field.
- Higher Resolution Sensors: Greater detail, better image clarity, superior enlargement capabilities.
- CCD Sensors: High-quality, low-noise images, perfect for still photography.
- CMOS Sensors: Cost-effective with better performance in speed-focused photography, enables burst shooting and video recording.
By understanding these elements, photographers can wield better control over their gear and make informed decisions, leading to superior photo quality.
Why Does the Size of the Image Sensor Matter?
The dimension of the camera image sensor plays an integral role in photography, as it impacts how much light the camera can process. Here's why size matters:
1. Light Capture: Larger image sensors have more and larger pixels, enabling them to capture a higher quantity of light. This results in images with less noise and superior performance in low-light conditions.

2. Image Noise: Smaller sensors, with their compact pixels, are more susceptible to image noise, especially in less-than-ideal lighting conditions. Essentially, the smaller the image sensor, the higher the probability of noise interference.
3. Dynamic Range: The sensor size influences the dynamic range of the camera - the span between the lightest and darkest elements it can capture without losing detail. Larger sensors typically present an enhanced dynamic range.
4. Depth of Field Control: With greater sensor size comes better control over depth of field. This is crucial for achieving those professional-looking shots where the subject is sharp, and the background is blurred.
5. Wide-Angle Options: If you’re keen on wide-angle photography, having a bigger sensor will be beneficial due to the lack of cropping factor, allowing capturing wider scenes.
In essence, while more significant image sensors can offer better control over depth of field, enhanced dynamic range, and improved low-light performance, they come at a higher cost. Conversely, smaller sensors might be more budget-friendly but may compromise on image quality due to higher noise levels and restricted dynamic range.
How to Choose the Right Sensor for Your Photography Needs?
Entering the world of photography necessitates an understanding of your requirements and preferences. Choosing a camera with the right image sensor is no different. Your decision inherently depends on the type of photography you wish to engage in, the quality of images you expect, and your budget. Here are some considerations to guide you in selecting the right sensor for your photography needs:
- Quality of Images: The quality of the image is significantly influenced by the sensor. Large, full-frame sensors are the prime choice for professionals who require exceptional image quality for detailed shots, picturesque landscapes, and scenes with low light.
- Budget Constraints: Each photography purchase should align with your budget. Full-frame sensors can be pricey. APS-C sensors, on the other hand, offer a more economical alternative. They maintain an appreciable balance between cost and quality, making them suitable for amateur or hobby photographers.
- Type of Photography: Your style of photography plays a pivotal role in sensor selection. Full-frame sensors provide an extensive dynamic range and depth-of-field control, ideal for landscape or portrait photography. However, if you are inclined toward action or high-speed photography, you will find CMOS sensors more appropriate due to their quick processing speed.
- Sensor's Tech Specs: Understand the type of image sensor technology used. CCD sensors generally provide clearer, more detailed images than CMOS sensors but may be more expensive.
By understanding these points, you can make a more informed decision about what sensor is the best fit for you. The perfect sensor is not only about size but also about resolution and technology. Remember, good photography is not necessarily about having the most high-end gear, but efficiently using what you have according to your needs. You can create extraordinary images with any sort of camera with its fundamentals well understood.
Conclusion
Understanding the importance of a camera image sensor is a key step towards taking better pictures. Remember that a good sensor is a blend of size, resolution, and technology. While larger, full-frame sensors offer better image quality, APS-C sensors provide a balance between cost and quality. Whether you are a professional or amateur photographer, learning about image sensors empowers you to make informed decisions to cater to your specific photography needs.
Related FAQs about what is a camera image sensor
What is the difference between CCD and CMOS image sensors?
CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) and CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) are the two main types of image sensors in digital cameras. CCD sensors are known for producing high-quality, low-noise images but are more expensive. Conversely, CMOS sensors are more affordable and efficient, offering improved performance for high-speed photography.
Can the type of image sensor affect low light performance of the camera?
Yes, the type of sensor significantly impacts a camera's low-light performance. Larger sensors, like full-frame sensors, capture more light and thus perform better in low-light conditions. They produce images with less noise as compared to smaller sensors, which are more prone to noise interference in such scenarios.
How does pixel count relate to image sensor in a camera?
Pixel count, expressed in megapixels (MP), is related to the image sensor as it indicates the number of light-sensitive dots on the sensor. Higher pixel count means greater image resolution, enabling more detail capture. It's important to note that pixel count must coincide with sensor size for optimal image quality.


